The unicist organizational approach is based on designing strategies and transforming them into actions using an object driven organization model. The object driven organization is the adaptive model that allows transforming strategies into an object driven architecture. It is a natural organization for institutionalized businesses.
The unicist object driven organization technology emulates the organization of nature to accelerate processes and save energy.
The Functionality of the Method
Institutionalization fosters, on the one hand, timeless strategies in order to ensure the permanence of a business and, on the other hand, short-term strategies to adapt to the conjunctures of the environment.
The final objective is to transform a business strategy into a business organization emulating the organization of nature. Nature, and any complex adaptive system, is organized by objects. This is evident when one sees the ecosystem or the organs of a human body.
In the field of business, the object driven organization is based on the design of the business processes, integrating business objects to achieve the strategic objectives that have been established. Objects are adaptive systems that have a concept that defines their purposes, have a value generating function and a quality assurance system that makes them reliable.
Only people who manage a process can use objects in a meaningful way. The example of an autopilot in an airplane makes this evident. An autopilot has limits where its use is functional and the pilot needs to reassume the process when these limits are being exceeded.
Benefit of the Object driven Organization
The use of Object Driven Organization and Client Centered Management saves +20% of the costs of business processes while increasing their level of effectiveness.
The unicist object driven organization is a result driven model that, according to the predefined objectives, designs the necessary processes and uses and reuses business objects to produce the expected results.
The object driven organization requires having a certain level of maturity in business. It can be defined as the organization of processes and the use of objects to achieve the objectives that have been established in a strategy. The Unicist Client Centered Management (UCCM) model catalyzes business and market expansion processes.
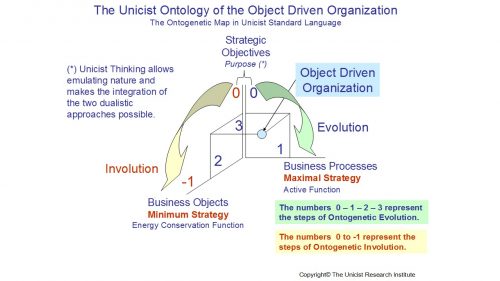
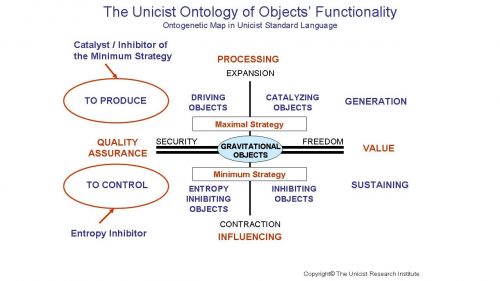
The Ontogenetic Map of the UODO
The goals that have been defined as possible by a strategic design are the input for the implementation of an object driven organization. These goals include a qualitative and quantitative definition in order to maintain the adaptability of the system.
The maximal strategy of the strategic objectives influences the roles that need to be defined and the minimum strategy defines the efficiency of the system that needs to be achieved.
The business processes drive the maximal strategy of this model while the business objects sustain the minimum strategy.
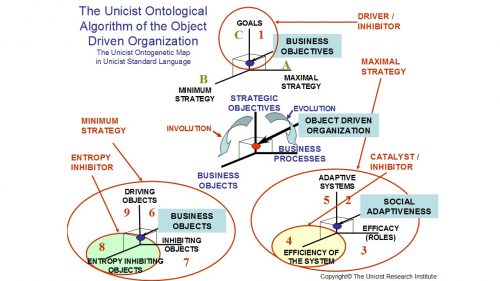
The Maximal Strategy
The purpose of the maximal strategy is the development of an adaptive system to manage the processes that are needed to achieve the goals that have been established. UODO is a universal adaptive model that applies to any institutionalized activity to produce results.
When the purpose of developing an adaptive system to manage the processes has been clarified, it becomes necessary to establish the roles that need to be organized to deal with the efficacy of the business processes.
After the roles have been defined, it becomes possible to define the efficiency of the processes, which implies the organization of a system that works as the catalyst of the UODO.
This model needs to be based on the definition of roles and an efficient system to sustain the adaptiveness of the maximal strategy.
The Minimum Strategy
The minimum strategy of the UODO is given by the use of business objects that sustain the processes. The first step to be developed is the definition of the driving objects that allow the achievement of the goals.
After the driving processes have been specified, it is necessary to define the inhibiting objects to be used to focus on the processes in order to ensure the functionality of the results.
Inhibiting objects are installed to define the limits of what is acceptable or not. They allow individuals to focus the energy on what needs to be done.
When the inhibitors have been defined, it is necessary to install entropy inhibiting objects that ensure that the limits of the functionality defined by the processes are not exceeded. These entropy inhibiting objects are the entropy inhibitors of the model and sustain the functionality of the driving objects installed in the processes.
The object driven organization can be considered complete when the business objects are installed and work within the business processes that have been organized to fulfill the maximal and minimum strategies.
This process requires making destructive and non-destructive pilot tests to confirm the validity of the organization.
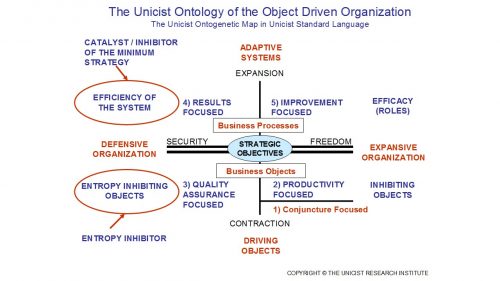
There are different levels of maturity of the UODO:
- Level 1) Conjuncture Focused
- Level 2) Productivity Focused
- Level 3) Quality Assurance Focused
- Level 4) Results Focused
- Level 5) Improvement Focused
Level 1) Conjuncture Focused
This level of organization is focused on solving the problems of the conjuncture. It is a short-term organization that is necessarily driven by the personal qualifications of the participants in a business process.
Each conjuncture is managed simultaneously as a threat and as an opportunity. There are no established roles for the participants. The relationships are managed based on subjective influences and the goal is to survive or take advantage of a situation.
There are no strategic goals established. This level of organization is driven by power and materialistic needs. This level cannot organize by objects and its evolution is basically driven by heroes.
The adaptive capacity of this organization is defined by the adaptive capacity of its members.
This level of organization cannot evolve to a superior level unless the organization is re-founded.
Level 2) Productivity Focused
This level of UODO is focused on improving the productivity. It organizes by objects in order to increase productivity and minimize costs.
Its main goal is to minimize the time of processes. It is based on installing business objects in functional organization processes in order to ensure their functionality and increase the speed of execution.
The timing of the processes is focused on the productive processes. The adaptive capacity of this organization is based on the use of mathematical tools that allow establishing patterns that are used to adapt to the environment.
This level of UODO is functional for massive production processes that need a low level of adaptiveness to the environment.
These organizations empower their adaptive capacity by the use of reliability systems and objective performance management systems. It allows managing stable markets and is based on operational strategies.
This level evolves to a superior level when the productivity that has been achieved allows managing a price leadership.
Level 3) Quality Assurance Focused
This level of UODO includes the preceding level and includes a quality assurance focus that allows introducing adaptive automation in the processes.
This adaptive automation includes a quality assurance system that allows establishing entropy inhibiting objects that avoid the loss of energy and the loss of the focus of the organization.
It is based on integrating the productivity of the preceding level with the quality of the processes. It includes the goals established by the strategic plan.
This level includes an incipient level of client orientation which drives the objectives of the quality assurance. It is natural for organizations that have a non-influential strategy, which requires influencing the environment through competitive prices and the quality of the products and services.
This level of UODO is based on a strong bureaucratic organization model compensated with an organization by objectives that allows members of the organization to participate in the establishment of such objectives. It is functional to operate in stable markets.
This level of organization evolves to a superior level when the quality and productivity of a company are the standard of the market or match the standards.
Level 4) Results Focused
This level of UODO includes the preceding level and is based on establishing a performance management system that allows monitoring the results of the company, the market and the shareholders.
This level establishes a strong focus on the market needs in order to ensure results. This focus implies establishing an efficient system that sustains the institutionalization of the company.
The people who participate in this company need to follow the strict rules of efficiency of the system, which need to be adaptive. This allows empowering the organization in order to manage the specific strategies that have been defined.
The level of adaptiveness is high and managed by the system. The system uses adaptive interfaces to manage the adaptive aspects of the business.
This level of UODO is based on a matrix organization that allows integrating the needs of the products and services with those of the market. It allows expanding markets when the organization has a dominant position.
This level of organization evolves to a superior level when the company establishes a dominant position in the market.
Level 5) Improvement Focused
This level of UODO includes the preceding level and is the most adaptive and effective type of organization. It is based on having an evolutionary model based on object driven process improvements.
Such improvements allow taking advantage of all the objects installed at the different levels improving them based on the changes that are needed to better adapt to the market and taking advantage of the new technologies that are available.
It requires integrating the non-adaptive aspects of the business that need to be upgraded in their efficiency with the adaptive aspects that need to become effective based on their efficacy.
The level of adaptiveness is adequate to the needs of the market, shareholders and stakeholders and its most significant characteristic is the organization by roles working as interdependent units.
The organization by roles empowers adaptiveness and allows optimizing processes. It requires having the necessary future scenarios in order to be able to plan long-term adaptive strategies. It also requires having established a universal strategic plan.
This superior level of organization needs to have corruption inhibitors in order to avoid its degradation.
UODO uses Unicist Client Centered Management
Nature, as a paradigmatic complex adaptive system, is organized by objects. The unicist organizational approach is based on emulating nature to manage businesses as adaptive systems.
The unicist object driven organization is the natural way to organize based on the knowledge of the ontogenetic maps of a business and its functions. It implies integrating business objects in the business processes that allow managing the adaptive aspects of businesses accelerating processes while saving energy.
Object driven marketing, object driven strategy, object driven management, object driven continuous improvement, object driven negotiation and object driven leadership are paradigmatic examples of the object driven organization.
This worked well when the influence of the actions allowed dominating the environment and failed when this was not the case.
UCCM is a management model that was developed to establish the rules for an optimum use of the company’s energy so as to satisfy its internal and external clients and catalyze business expansion. When talking about the external client in the company we necessarily refer to the customer and the shareholder. UCCM is a model to provide result-assurance, client orientation and secure added value to an organization. It is the natural model to expand businesses.
Client Centered Management: the model to grow
Unicist Client Centered Management is a model that catalyzes market expansion processes. It is part of the unicist natural organization model. The natural organization is a meta-model in itself that integrates the organization that is needed for the business and the market, the client orientation and the personalization of the work processes.
Client Centered Management needs to be established to drive actions towards the end client and then the personal organization needs to be used in order to ensure the fulfillment of the organizational roles.
The functionality of the Client Centered Management model is driven and catalyzed by the use of business objects that save energy and make processes simpler and more effective.
Thus CCM is the natural model for business expansion. It has to be considered that it requires business objects driven processes and a role model that allows managing responsibilities.
The Client Centered Management Model
Client Centered Management is a breakthrough and a back to basics to provide an adequate environment to grow. It is a management model that was developed to establish the rules for an optimum use of the company’s energy so as to satisfy its internal and external clients. When talking about the external client in the company we necessarily refer to the customer and the shareholder.
UCCM is a model to provide result-assurance, client orientation and secure added value to an organization. It is the natural model to expand businesses.
The principles that integrate the UCCM model are:
Purpose: Results Assurance
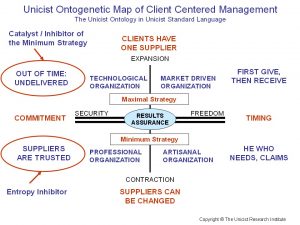
1. Divide the processes into client-supplier units
This division aims at determining which operating units have a clear “output” so as to be suppliers and which have a clear “input” so as to be considered clients.
2. Minimize intermediaries
This principle follows the natural concept of “the larger the number of intermediaries, the bigger the entropy”.
3. Services or products received are paid for
This principle makes the organization become more aware of costs and benefits and enables negotiating goals to obtain measurable and predictable results.
Maximal Strategy: Client Orientation
4. Each client has only one supplier
The principle that each client has only one supplier defines the role of the supplier which drives towards a solution driven approach and not only a task driven approach.
5. First giving, then receiving
It implies that services are paid for once rendered and not during the rendering process or in advance. There can be grounded exceptions to this in the organization.
6. Delivered out of time is considered undelivered
In practice, it ends up in an incentive system for each delivery on time and a punishment system if the dispatch is made out of time.
Minimum Strategy: Added Value Assurance
7. Every client may change his supplier
The organization’s success is given by its capacity to satisfy the clients’ needs. This obliges the organization to manage the unfulfilled situations a supplier may have.
8. He who needs claims
“He who needs claims” is a principle based on the KANBAN approach which is closely associated with the natural tendency of satisfying one’s own needs.
9. Each supplier counts on his client’s trust
One of the basic principles of any successful large company is having a high reliability level. Reliability and trust are “sine qua non” principles for UCCM’s application.
Some considerations on objects
Objects are productive adaptive units that have a concept, an added value, the necessary quality assurance and a methodology to ensure the minimum strategy. To imagine an object please consider an automatic pilot in an airplane. It can be considered a “paradigmatic” object.
We would like to make a clarification of the difference between objects and things.
Objects only exist within a process. When they are not part of a process they are things.
Objects produce an added value for someone in the process. When they do not produce added value they are things. Things can be such in some conditions and objects in others. The definition of an “object” is functional to a value that needs to be achieved.
For example, a commercial car is an object if there is a driver, if not it is a thing. But if it is a collection car it is an object for the owner and for those who appreciate its value. For those who do not, it is just a thing.
In the world of abstract objects a rumor is an object if it achieves the expected value. News is an object if it has a use for the one who receives it.
That is why it has to be clarified that objects depend on a given functionality within a process. A stone might be an object if it has a use, if not, it is just a thing.
That is why only people who have a sound knowledge on a process can design the objects that are part of the process.
In order to reuse objects in other homologous processes it becomes necessary to have an expert knowledge. Without it no homologies can be understood.
There are different types of objects:
- Driving Objects
To drive processes - Catalyzing Objects
To accelerate processes - Entropy Inhibiting Objects
To inhibit the entropy of business processes - Inhibiting Objects
To inhibit dysfunctional events in a business - Gravitational Objects
To influence the results of processes
About the Driving Business Objects
The function of driving business objects is to achieve the concept that underlies their creation. To do so they need to generate added value and have a quality assurance system that ensures the value they add. The quality assurance system can be an automated system -in case of systemic objects- or a human dependant control system -in case of operational objects.
About the Inhibiting Business Objects
The purpose of Inhibiting Business Objects is to sustain the focus of the concept that underlies the driving objects. By establishing the focus, they need to inhibit any activity that is beyond this focus. Although these objects are based on fostering a commitment with results in order to fulfill their functionality, their core aspect is the quality assurance of the focus which sustains their inhibiting activity.
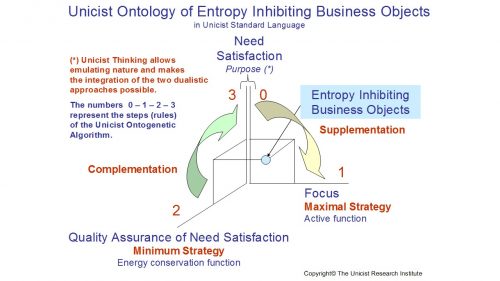
About the Entropy Inhibiting Business Objects
Entropy inhibiting business objects seek to ensure that the need of a process is satisfied. Their active function is to ensure that the focus on the needs is maintained. They provide the control function of objects and are complementary with the driving objects in order to ensure that the solution of the concept is being achieved.
About the Catalyzing Business Objects
Catalyzing business objects are elements of the restricted context of a system that can be used to influence other objects to accelerate their work. They are not part of the system they accelerate. Catalyzing objects are energy conservation functions of a superior level that influence the use of the energy of a system. Their main characteristic is that they need to have the necessary synchronicity, acceleration and speed to work when they are needed. An example of this a catalyst is the brand power when it is used in selling processes. They need to be designed with an intrinsic ambiguity in order to allow the participants to decide to accelerate. If they are not ambiguous they do not work as catalysts and produce paradoxical results.
About the Gravitational Business Objects
Gravitational Objects impose an authoritative context in order to foster freedom of individuals and provide a framework of security to influence individuals’ actions. They need to be based on subliminal design and an adequate level of participation in order to ensure that leadership can be accepted. They represent the wide context that influences the restricted context and thus the system.
An example of a gravitational object is the use of Corporate Universities to provide upgrades to members of the market. But these Corporate Universities need to work at a higher academic level than the one necessary to manage the processes and objects of a system.
They need to be separated from the catalysts and from the objects of the system in order to work independently from them.
Other examples are the philanthropic activities of corporations.
The Use of Business Objects
Some of the companies that use objects are: Airbus, Amazon, Apple, BBC, Boeing, Dassault Systemes, Dupont, Ericsson, Facebook, General Electric, Google, Hilton, Honda, Hyundai, LinkedIn, Lufthansa, Mapfre, Mayo Clinic, Michelin, Novartis, Open Text, P&G, Pfizer, SAP, Siemens, Tata Motors, Toyota, Unilever, Walmart, Walt Disney World and Youtube.
Annex
Expert Systems to Sustain Methods
The unicist expert systems are alternative tools for any method that deals with business problem solving or solution building.
They were developed to manage the fundamentals of business processes by managing the root causes of processes to develop solutions in adaptive environments.
With multiple specialized modules to solve specific problems, these systems manage the unified field of the business processes to manage their functionality, dynamics and adaptability.
Note: The R&D work of this technology/methodology was led by Peter Belohlavek at The Unicist Research Institute.
The Unicist Research Institute